A monitor is a relatively small warship that is neither fast nor strongly armored but carries disproportionately large guns. They were used by some navies from the 1860s, during the First World War and with limited use in the Second World War. The original monitor was designed in 1861 by John Ericsson, who named it USS Monitor. Subsequent vessels of this type were accordingly classed as “monitors”. They were designed for shallow waters and served as coastal ships. The term also encompassed more flexible breastwork monitors, and was sometimes used as a generic term for any turreted ship.
In the early 20th century, the term was revived for shallow-draught armoured shore bombardment vessels, particularly those of the Royal Navy: the Lord Clive-class monitors carried guns firing heavier shells than any other warship ever has, seeing action (albeit briefly) against German targets during World War I. The Lord Clive vessels were scrapped in the 1920s.
The term “monitor” also encompasses the strongest of riverine warcraft, known as river monitors. During the Vietnam War these much smaller craft were used by the United States Navy. The Brazilian Navy’s Parnaíba and the Romanian Navy’s three Mihail Kogălniceanu-class river monitors are among the last monitors in service.
Humber class
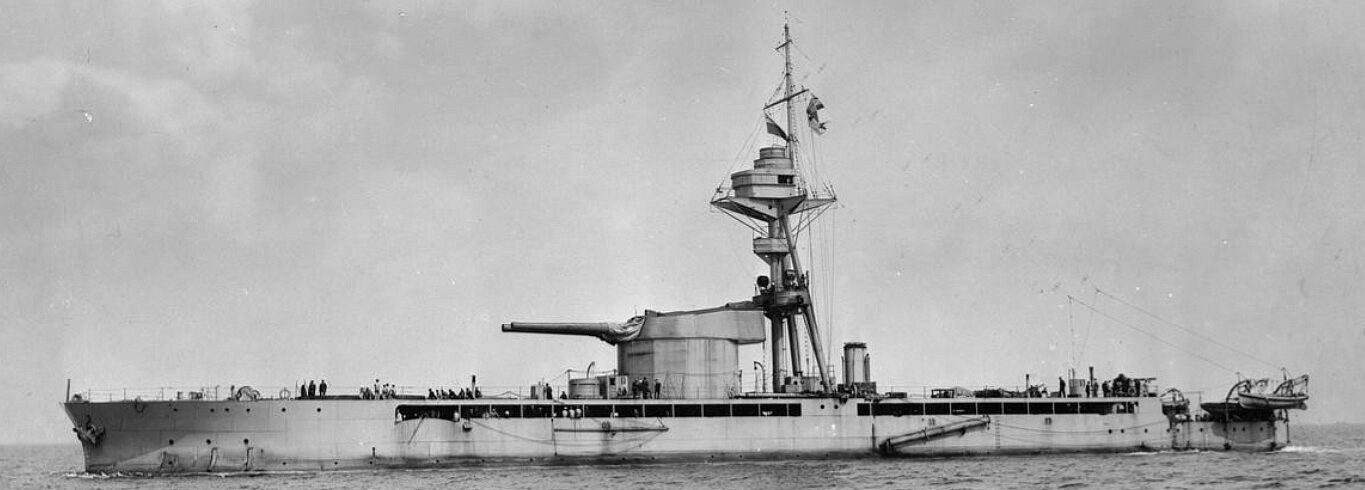
The Humber-class monitors were three large gunboats under construction for the Brazilian Navy in Britain in 1913. Designed for service on the Amazon River, the ships were of shallow draft and heavy armament and were ideally suited to inshore, riverine and coastal work but unsuitable for service at sea. The class comprised Humber, Mersey and Severn. All three were taken over by the Royal Navy shortly before the outbreak of the First World War and were commissioned as small monitors. All three saw extensive service during the war and were sold in 1919. After decommissioning the HMS Humber was sold and converted to a crane vessel.
Hull | Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Status |
-- | HMS Humber (ex Javary, Brazil) | Humber class | 08-08-1914 | 17-09-1920 | Sold to F. Rijsdijk for use as a crane lighter |
-- | HMS Mersey (ex Madeira, Brazil) | Humber class | 03-08-1914 | 1921 | Sold for scrap 1921 |
-- | HMS Servern (ex Solimoes, Brazil) | Humber class | 08-08-1914 | 09-05-1921 | Sold for scrap 1921 |
Abercrombie class
Soon after the outbreak of World war I the president of the Bethlehem Steel company contacted Winston Churchill the First Lord of the admiralty. He offered for sale Four Twin Turrets armed with two 14-inch Guns in each. Winston Churchill saw the possibility because the Royal navy were in need of shallow draft ships with the armament for heavy shore bombardment. The ships were built according the latest designs but ultimately turned out to be very unwieldy and slow. Initially they were called the Styx class but soon were allocated M1 – to M4. In February 1915 they give them American names to acknowledge the guns US Origins. M1 was to be Admiral Farragut, M2 General Grant, M3 was to be Robert E Lee M4 was to be Stonewall Jackson. But because the guns were sold to Britain, which was a flagrant breach of US neutrality they were renamed as shown in the list below These four ships had been designed to carry seaplanes but did not carry them for very long as it was found that land based aircraft called do naval sea spotting more efficiently,
Hull | Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Status |
-- | HMS Abercrombie | Abercrombie class | 01-05-1915 | 17-09-1920 | Sold for scrap 25-06-1927 |
-- | HMS Havelock | Abercrombie class | 01-05-1915 | may 1919 | Sold for scrap 25-06-1921 |
-- | HMS Raglan | Abercrombie class | 01-05-1915 | -- | Sunk 20-01-1918 |
-- | HMS Roberts | Abercrombie class | 21-05-1915 | 26-05-1919 | Sold for scrap September 1936 |
Lord Clive class
The eight monitors of the Lord Clive class were basically repeats of the Abercrombie class monitors, but armed with British 12 inch guns instead of the 14 inch American guns used on the earlier ships. Their guns were taken from the Majestic class battleships, then the oldest pre-dreadnought battleships still in service. Like the earlier Abercrombie class the Lord Clive class ships were underpowered, with a top speed in service of 6.5kts, but this was not a class of ship that greatly benefited from high speeds.
Hull | Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Status |
478 | HMS Lord Clive | Lord Clive class | 10-07-1915 | 26-11-1918 | Sold for scrap 10-10-1927 |
479 | HMS General Craufurd | Lord Clive class | -- | -- | Sold for scrap 09-05-1921 |
480 | HMS Earl of Peterborough | Lord Clive class | -- | 1921 | Sold for scrap 1921 |
481 | HMS Sir Thomas Picton | Lord Clive class | -- | 1921 | Sold for scrap 1921 |
477 | HMS Prince Eugene | Lord Clive class | 21-08-1915 | 1919 | Sold for scrap 09-05-1921 |
-- | HMS Prince Rupert | Lord Clive class | -- | 1923 | Sold for scrap 1923 |
469 | HMS Sir John Moore | Lord Clive class | 22-07-1915 | 1921 | Sold for scrap 08-11-1921 |
-- | HMS General Wolfe | Lord Clive class | 27-10-1915 | 1919 | Sold for scrap 1923 |
Marshal Ney class
The Marshal Ney Class of monitor (sometimes known as the Marshals) was the first in the Royal Navy to be armed with the 15-inch gun. The two ships, Marshal Ney and Marshal Soult were also one of the first classes of British warship to be powered by diesel engine.
Hull | Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Status |
(M.14) | HMS Marshal Soult | Marshal Ney class | August 1915 | -- | Renamed from M.14, Sold for scrap 10-07-1946 |
859, (M.13) | HMS Marshal Ney | Marshal Ney class | 31-08-1915 | September 1919 | Renamed from M.13, Sold for scrap 06-10-1921 |
Gorgon class
The Gorgon class monitors were a class of monitors in service with the Royal Navy during World War I. Gorgon and her sister ship Glatton were originally built as coastal defence ships for the Royal Norwegian Navy, as HNoMS Nidaros and HNoMS Bjørgvin respectively but requisitioned for British use. Gorgon commissioned first, in June 1918 and bombarded German positions and other targets in Occupied Flanders. She was offered for sale after the war, but was used as a target ship when there were no takers. She was sold for scrap in 1928. Glatton was destroyed by a magazine explosion only days after she was completed in September 1918.
Hull | Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Status |
-- | HMS Gorgon (ex-Nidaros) | Gorgon class | 01-05-1918 | September 1919 | Renamed from M.14, Sold for scrap 10-07-1946 |
-- | HMS Glatton (ex-Bjørgvin) | Gorgon class | 31-08-1918 | -- | Wrecked by explosion, 16-09-1918 |
M15 class
The M15 class comprised fourteen monitors of the Royal Navy, all built and launched during 1915. The ships of this class were ordered in March, 1915, as part of the Emergency War Programme of ship construction. They were designed to use the 9.2 inch Mk VI gun turrets.
Hull | Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Status |
M15 | HMS M15 | M15 class | June 1915 | -- | Sunk 11-11-1917 |
M16 | HMS M16 | M15 class | June 1915 | -- | Sold 29-01-1920 |
M17 | HMS M17 | M15 class | June 1915 | -- | Sold 12-05-1920 |
M18 | HMS M18 | M15 class | July 1915 | -- | Sold 29-01-1920 |
M19 | HMS M19 | M15 class | June 1915 | -- | Sold 12-05-1920 |
M20 | HMS M20 | M15 class | July 1915 | -- | Sold 20-1-1920 |
M21 | HMS M21 | M15 class | July 1915 | -- | Sunk 20-10-1918 |
M22 | HMS M22 | M15 class | August 1915 | -- | Sold Decemeber 1938, Wrecked 02-01-1939 |
M23 | HMS M23 | M15 class | July 2015 | -- | Broken up 1959 |
M24 | HMS M24 | M15 class | August 1915 | -- | Sold 29-01-1920 |
M25 | HMS M25 | M15 class | September 1915 | -- | Scuttled 16-09-1919 |
M26 | HMS M26 | M15 class | October 1915 | -- | Sold 20-01-1920 |
M27 | HMS M27 | M15 class | November 1915 | -- | Scuttled 16-09-1919 |
M28 | HMS M28 | M15 class | August 1915 | -- | Sunk 20-01-1918, 11 killed |
M29 class
The M29 class is a monitor ship following the M15 class. It is a ship with two 152.4 mm guns mounted on it with a very small displacement of 535 tons. Unlike the monitor ships that appeared later, it did not have the firepower of a battleship because it had artillery for secondary artillery, but it was usable enough for ground support fire. In fact, it was created for that purpose and was put to good use. Five ships were built, from HMS M29 to HMS M33.
Hull | Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Status |
M29 | HMS M29 | M29 class | June 1915 | -- | Converted to minelayer, repair and depot vessel, Sold for scrap december 1946 |
M30 | HMS M30 | M29 class | June 1915 | -- | Sunk 14-05-1916 |
M31 | HMS M31 | M29 class | July 1915 | -- | Converted to minelayer and torpedo training vessel, Sold for scap 1948 |
M32 | HMS M32 | M29 class | June 1915 | -- | Sold janyary 1920 for use as a oil tanker |
M33 | HMS M33 | M29 class | June 1915 | -- | Sold to minelayer, fuelling hulk and currently museum ship in Portsmouth |
Erebus class
The Erebus class of warships was a class of 20th century Royal Navy monitors armed with a main battery of two 15-inch /42 Mk 1 guns in a single turret. It consisted of two vessels, Erebus and Terror, named after the two ships lost in the Franklin Expedition. Both were launched in 1916 and saw active service in World War I off the Belgian coast. After being placed in reserve between the wars, they served in World War II, with Terror being lost in 1941 and Erebus surviving to be scrapped in 1946.
Hull | Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Status |
I02 | HMS Erebus | Erebus class | June 1915 | -- | Scrapped july 1946 |
I03 | HMS Terror | Erebus class | June 1915 | -- | Scuttled 24-02-1941 |
Roberts class
The Roberts class of minitors of the Royal Navy consisted of two heavily gunned vessels built during the Second World War. They were the HMS Roberts, completed in 1941, and Abercrombie, completed in 1943.
Features of the class were two 15-inch guns in a twin turret, shallow draught for operating inshore, broad beam to give stability (and also resistance to torpedoes and mines) and a high observation platform to observe fall of shot.
Hull | Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Status |
F40 | HMS Roberts | Roberts class | 02-09-1916 | -- | Sold for scrap June 1965 |
F109 | HMS Abercombie | Roberts class | 22-07-1916 | -- | Scrapped 24 December 1954 |
References:
1. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_monitors_of_the_Royal_Navy





































