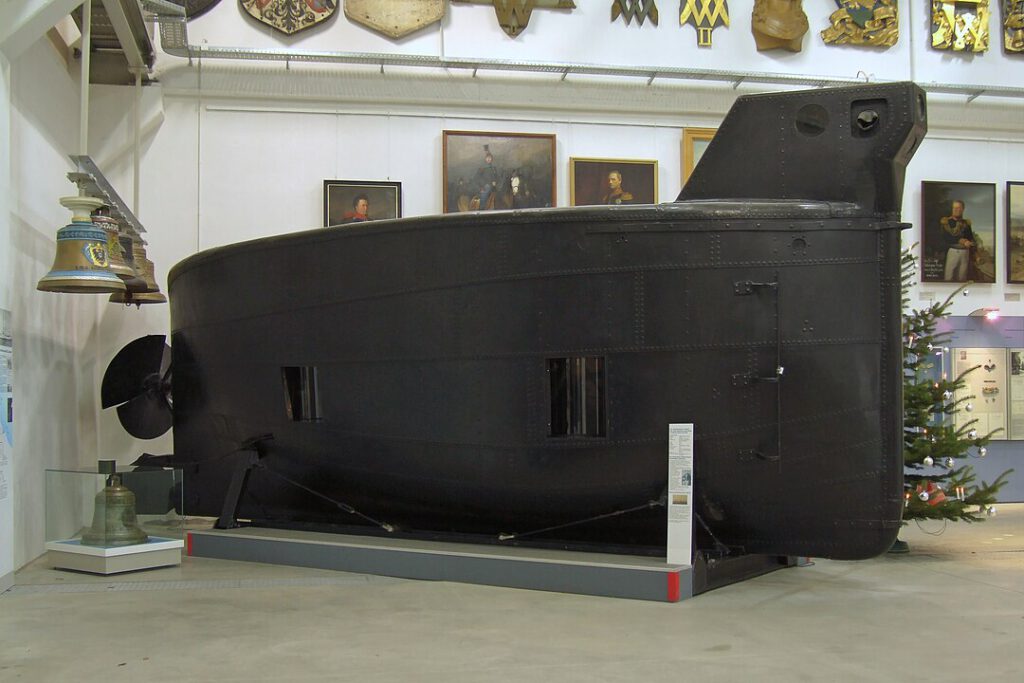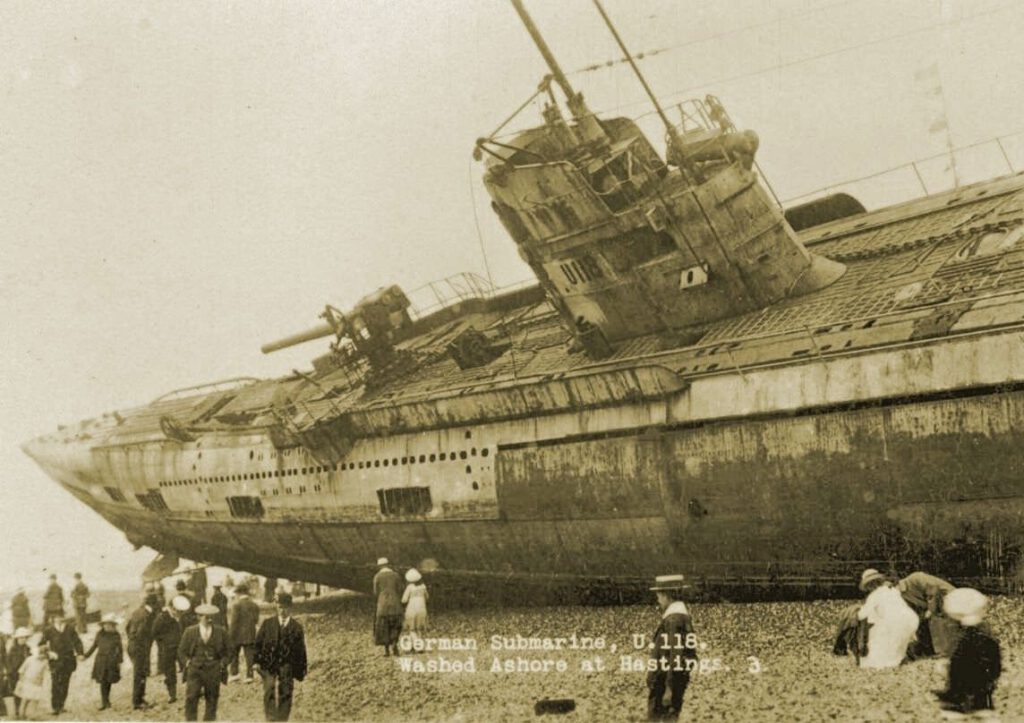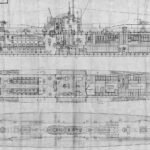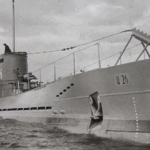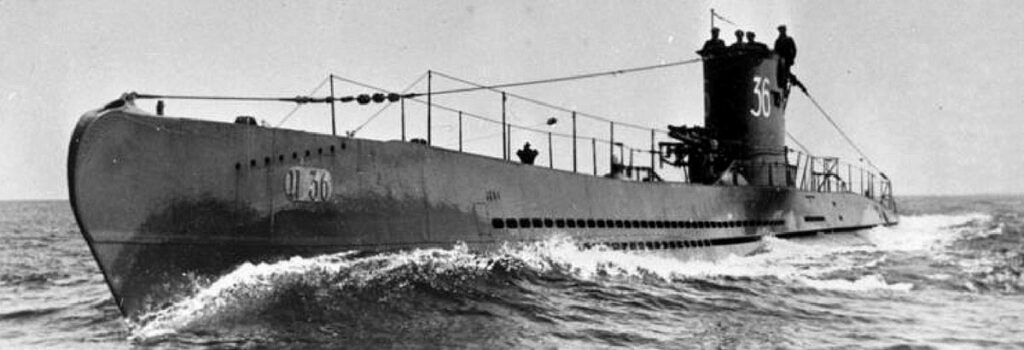
German submarines, or U-boats (Unterseeboat), evolved from early experimental prototypes like the Brandtaucher (1850) and functional Forelle (1903) in formidable naval weapons in World War I and II. Their prominent roles in both World Wars, where they were primarily used to sink enemy shipping and disrupt trade routes through torpedo attacks.. They were a major factor in bringing the United States into World War I and posed a severe threat to Allied supply lines in World War II. The history includes early submarine development, the massive but ultimately costly U-boat campaigns, and the eventual surrender of most of the fleet after the wars. Their impact forced major strategic shifts, leading to significant Allied losses but also driving innovations in submarine technology, like advanced diesel engines and snorkels, making them key players in naval warfare history.
Germany has commissioned over 1,500 U-boats (German: Unterseeboot) into its various navies from 1906 to the present day. The submarines have usually been designated with a U followed by a number, although World War I coastal submarines and coastal minelaying submarines used the UB and UC prefixes, respectively. When Germany resumed building submarines in the 1930s, the numbering of the submarines was restarted at 1. The renumbering was restarted at 1 a third time when Germany resumed building submarines in the 1960s.
World War I:
- Early development: Germany’s first submarine, the Brandtaucher, sank in 1851, but the first functional German submarine, the Forelle, was built in 1903.
- Naval integration: The first submarine commissioned by the German Navy was the SM U-1 in 1906, followed by the more advanced SM U-19 in 1912, which featured a more powerful diesel engine.
- Warfare: U-boats achieved significant successes against Allied warships and merchant ships.
- Unrestricted submarine warfare: In 1915, Germany began unrestricted submarine warfare, which was temporarily suspended due to U.S. protests, but resumed in February 1917.
- U.S. entry: The U-boat campaign was a significant factor in the United States entering the war.
- Post-war: The surviving U-boats were surrendered under the Treaty of Versailles, which aimed to prevent Germany from threatening British trade again.
World War II:
- Resumption of service: Germany built 1,162 U-boats for this war.
- “Happy Time”: From mid-1940 to early 1942, U-boats inflicted heavy losses on Allied and neutral shipping, a period known as the “happy time”.
- Strategic goal: The goal was to sever Britain’s supply lines to force it out of the war.
- Shift in balance: The entry of the United States and the subsequent increase in ship production, particularly the Liberty ships, shifted the balance of power against the U-boats.
- Technological advancements: Germany developed advanced U-boat classes like the Type VII and Type IX, which featured improved capabilities like longer range and more effective torpedoes.
- Atlantic U-boat bases: Germany established massive U-boat bases in occupied France, such as those at Lorient and Saint-Nazaire, which gave their submarines a significant advantage in the Atlantic.
- Defeat: By 1943, the U-boats were vulnerable, and by the end of the war, most were destroyed, surrendered, or scuttled.
Post-war:
- Surviving U-boats were taken as war prizes by the Allied powers and served in navies such as those of the United Kingdom, France, and the Soviet Union.
World War I – era
There were some 380 U-boats commissioned into the Kaiserliche Marine in the years before and during World War I. Although the first four German U-boats U-1, U-2, U-3, and U-4 were commissioned before 1910, all four served in a training capacity during the war. German U-boats used during World War I were divided into three series. The U designation was generally reserved for ocean-going attack torpedo U-boats. The UB designation was used for coastal attack U-boats, while the UC designation was reserved for coastal minelaying U-boats.
Class | No. build | Commissioned | Notes |
U 1 | 1 | 14-12-1906 | SM U-1 is the first U-boat produced for the German Empire's Imperial German Navy. |
U 2 | 1 | 18-07-1908 | SM U-2 was a vast improvement over her predecessor SM U-1 |
U 3 | 2 | 1909 | Type U 3 subs had more powerfull engines than the previous U 2 and were more reliable. |
U 5 | 4 | 1910 - 1911 | All lost |
U 9 | 4 | 1910 - 1911 | Lost 3 |
U 13 | 3 | 1912 | Lost 3 |
U 16 | 1 | 28-12-1911 | U-16 was a pre-war U-boat, served up to 1915 when she was utilized as a training submarine. |
U 17 | 2 | 1912 | Lost 1 |
U 19 | 4 | 1913 | The first subs with Diesel engines for surface propulsion and charging the batteries. |
U 23 | 4 | 1913 - 1914 | Lost 2 |
U 27 | 4 | 1914 | Lost 3, They were very similar to the preceding Type U 19 and Type U 23. |
U 31 | 12 | 1915 - 1919 | Lost 7, German Type U 31 submarines were double-hulled ocean-going submarines |
U 43 | 7 | 1915 - 1916 | Lost 6, he Type U43 was the continuation of previous double-hull U-boats design |
U 51 | 6 | 1916 | Lost 2 |
U 57 | 12 | 1916 - 1917 | Lost 7 |
U 63 | 3 | 1916 | Lost 2 |
U 66 (UD) | 5 | 1915 | Lost 3, The class is alternately referred to as the U-66 class or the Type UD. |
UE I | 10 | 1915 - 1916 | Lost 7, The UE I submarine were ocean-going single-hull submarines with saddle tanks |
U 81 | 6 | 1916 | Lost 4, Type 81 U-boats carried 12 torpedoes and had various arrangements of deck guns. |
U 87 | 6 | 1917 | Lost 4, Type 87 U-boats carried 16 torpedoes and had various arrangements of deck guns. |
U 93 | 24 | 1917 - 1919 | Lost 6, |
U 115 | 2 | -- | Never completed |
UE II | 10 | 1918 | Lost 6, UE II boats carried 14 torpedoes and were armed with one 150 mm deck gun. |
U 127 | 8 | -- | Never completed |
U 135 | 4 | 1918 | Planned 8, Completed 2, canceled 6 |
U 139 | 3 | 1918 | U-139, originally designated "Project 46", long-range U-boats built during World War I. |
U 142 | 9 | 1918 | It notably served as a template for the Imperial Japanese Navy's "Junsen type submarines". |
U 151 | 7 | 1917 | Type U 151, a class of large, long-range submarines initially constructed as a merchant sub. |
U 158 | 2 | 1918 | The war ended before they could see active service, and they were broken up in 1919. |

Coastal U-Boats (UB)
Coastal attack torpedo U-boats were smaller craft intended for operation closer to land. They were designated with a UB prefix.
Class | No. build | Commissioned | Notes |
UB I | 20 | 1915 | Lost 10, Type UB I was a class of small coastal submarines at the beginning of WW I. |
UB II | 38 | 1915 - 1916 | Lost 21, Type UB II class was twice as large as the preceding type UB I. |
UB III | 96 | 1917 - 1919 | Planned 201, building 145, 96 completed, 56 cancelled, 37 lost |
Coastal Minelaying U-Boats (UC)
Coastal minelaying U-boats were smaller vessels intended to mine enemy harbors and approaches. They were designated with a UC prefix.
Class | No. build | Commissioned | Notes |
UC I | 15 | 1915 | Completed 15, Lost 14, The UC I submarines were a class of small minelaying U-boats. |
UC II | 38 | 1916 - 1917 | Completed 64, lost 47, Significant improvement over the preceding Type UC I |
UC III | 96 | 1917 - 1919 | Planned 113, completed 25, lost 1 |
Foreign U boats (WW I)
At the outbreak of World War I Germany took charge of a number of submarines under construction in German shipyards for other countries.
U-boat | No. build | Commissioned | Notes |
SM UA | 1 | 14-08-1914 | Ex-Norwegian A-class submarine A-5 |
U-66 - U-70 | 4 | -- | Ex-Austro-Hungarian U-7 class U-7 to U-11 |
US-1 | 1 | -- | Ex-Russian Bars class Burevestnik, only test run - not in service |
US-2 | 1 | -- | Ex-Russian Bars class Orlan, Commissioned later abandoned to White Russian Forces |
US-3 | 1 | -- | Ex-Russian Bars class Utka, only test run - not in service |
US-4 | 1 | -- | Ex-Russian Bars class Gagara, only test run - not in service |
No reliable pictures availebale of the Foreign U-Boats.
World War II U-Boats
In the World War II era, Germany commissioned some 1,250 U-boats into the Kriegsmarine. The German military submarines known as U-boats that were in action during World War II were built between 1935 and 1944, and were numbered in sequence from U-1 upwards. Numbering was according to the sequence in which construction orders were allocated to the individual shipyards, rather than commissioning date; thus some boats carrying high numbers were commissioned well before boats with lower numbers. Later in the war, whole contracts for older designs were sometimes cancelled in favour of newer designs, with the numbers allocated being reused later.
Class | No. build | Commissioned | Notes |
Type I | 2 | 1936 | Type I was the first post–WW I attempt to produce an oceangoing sub for Nazi Germany |
Type IIA | 6 | 1934 - 1935 | The Type IIA was a single hull, all welded boat with internal ballast tanks. |
Type IIB | 20 | 1935 - 1940 | The Type IIB was a lengthened version of the Type IIA. |
Type IIC | 8 | 1938 - 1940 | The Type IIC was a further lengthened version of the Type IIB. |
Type IID | 16 | 1940 - 1941 | The Type IID had additional saddle tanks fitted to the sides of the external hull. |
Type VIIA | 10 | 1936 | Type VII was a class of medium attack U-boats built for Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. |
Type VIIB | 24 | 1938 - 1940 | The type VIIB is an improved version of the Type I and Type VII U-boats. |
Type VIIC | 581 | 1940 - 1944 | The Type VIIC design was the same of Type VIIB but a extra sonar room was created. |
Tyope VIIC/41 | 125 | 1943 - 1945 | Same as the Type VIIC but an improved performance design |
Type VIID | 6 | 1941 - 1942 | Type VIID were the same as their Type VIIC sisterships, with benefits of extra range. |
Type VIIE | 0 | -- | Type VIIE was a project for trying out lightweight diesel engines. Construction did not start. |
Type VIIF | 4 | 1943 | Type VIIF but was with 1,084 t (1,067 long tons) much heavier. Without loosing much speed. |
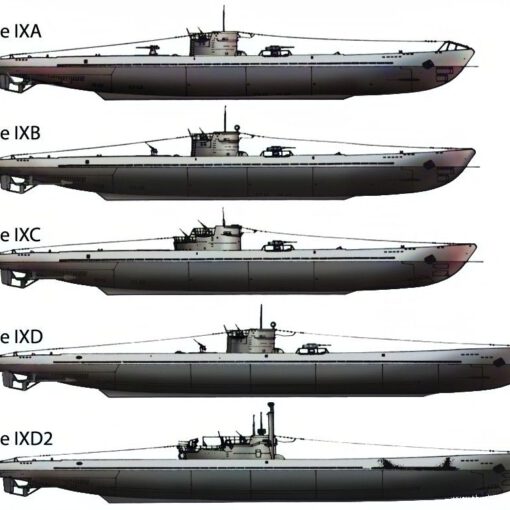
Type IXA | 8 | 1938 - 1939 | Type IXA submarines were intended to be fairly large ocean-going submarines. |
Type IXB | 14 | 1939 - 1940 | Thirteen were sunk in the course of the war, the remaining one was decommissioned. |
Type IXC | 54 | 1941 - 1942 | Type IXC had a wider outer hull, with storage for more fuel, increasing the boat's range. |
Tyoe IXC/40 | 87 | 1942 - 1944 | Type IXC/40 was an improved Type IXC with slightly increased range. |
Tyoe IXD | 32 | 1942 - 1944 | The Type IXD was significantly longer and heavier than the IXC/40. |
Tyope X (XB) | 8 | 1941 - 1944 | Originally a long-range minelayer, the Type X were later used as long-range cargo transports. |
Type XI | -- | -- | The Type XI was a planned artillery boat but were cancelled at the outbreak of WWII. |
Type XIV | 17 | 1941 - 1943 | 24 were planned, only 10 were commissioned, 3 were cancelled and 11 never laid down. |
Type XVIIA | 4 | 1943 - 1944 | Type XVII U-boats were small coastal submarines. |
Type XVIIB | 3 | 1944 - 1945 | 12 Type XVIIB submarines were planned, but only three were completed. |
Type XVIIK | 1 | -- | Was still incomplete in May 1945. |
Type XCVIII | 2 | 1944 | Type XVIII was a projected attack boat using the Walter propulsion system. 1 canceled. |
Type XXI | 118 | 1944 - 1945 | Type XXI were a class of diesel–electric submarines, 118 were completed. |
Type XXII | 61 | 1944 - 1945 | Type XXIII were ("electric boats"). They were small coastal submarines. |
Midget submarines
A midget submarine is any submarine under 150 tons, typically operated by a crew of one or two but sometimes up to six or
nine, with little or no on-board living accommodation. They normally work with mother ships, from which they are launched and recovered and which provide living accommodation for the crew and support staff. Military types work with surface ships and other submarines as mother ships. Midget submarines are best known for harbor penetration. Germany’s various World War II designs were mostly designed to attack Allied shipping off landing beaches and harbors, although the Seehund had a great enough range to attack shipping off the Thames estuary. Midget submarines are commonly armed with torpedoes and mines in the form of, for example, detachable side loads and nose sections. Alternatively they may function as swimmer delivery vehicles to deliver frogmen to the vicinity of their targets, which are then attacked with limpet mines.
Class | No. build | Commissioned | Notes |
Biber class | 324 | 1944 | |
Molch class | 393 | 1944 | Molch was an unsuccessful series of one-man submarines created during World War II. |
Seehund class | 285 | 1944-1945 | Lost 35, active 138, Seehund also known as Type XXVII, operated by two-man crews. |
Biber class
The Biber (German for “beaver”) was a German midget submarine of the Second World War. Armed with two externally mounted 53-centimetre (21 in) torpedoes or mines, they were intended to attack coastal shipping. They were among the smallest submarines in the Kriegsmarine. The Biber was hastily developed to help meet the threat of an Allied invasion of Europe. This resulted in basic technical flaws that, combined with the inadequate training of their operators, meant they never posed a real threat to Allied shipping, despite 324 submarines being delivered. One of the class’s few successes was the sinking of the cargo ship Alan-A-Dale.
Several survive in museums, including one in operational condition.
Molch class
The Molch (german for “newt” or “salamander”) was an unsuccessful series of one-man midget submarines created during World War II. Built in 1944, it was the first mini-submarine of Nazi Germany’s Kriegsmarine, but was not successful in combat operations and suffered heavy losses. The Molch was based on torpedo technology, and carried two G7e torpedoes attached externally on either side of the craft. It was fully electrical and was created for coastal operations, with a range of 64 km. The front section of the boat held a large battery. The operator sat between two small trimming tanks behind the battery. Behind the operator was the electric motor. The complicated system of tanks made it difficult to control during combat.
Seehund class
Seehund (German for “seal”), also known as Type XXVII, was a midget submarine built by Nazi Germany during World War II. Designed in 1944 and operated by two-man crews, it was used by the Kriegsmarine during the closing months of the war, sinking nine merchant vessels and damaging an additional three, while losing 35 boats, mostly attributed to bad weather. The French Navy used four captured boats after the war until 1953. The origin of the Seehund began with the salvage of the two British X class submarines HMS X6 and X7 which had been lost by the Royal Navy during Operation Source, an attempt to sink the German battleship Tirpitz. Hauptamt Kriegschiffbau subsequently produced a design for a two-man submarine based on inspection of the British boats, designated Type XXVIIA and named Hecht (“Pike”).
Foreign U-Boats (WW II)
Foreign U-boats was the title for a special section created by Nazi Germany’s Kriegsmarine that adopted 13 captured enemy submarines and a single Turkish vessel into the U-boat corps. Beginning in 1939 and lasting until the end of World War II in 1945, the Kriegsmarine modified a total of 13 captured enemy submarines, then deployed them into combat with German crews. The special corps was not especially successful, as only ten enemy ships were destroyed by Foreign U-boats
through the entire war.
New Hull | Origin |
UA | Turkish submarine Batiray |
UB | British submarine HMS Seal (N37) |
UC-1 | Norwegian submarine HNoMS B-5 |
UC-2 | Norwegian submarine HNoMS B-6 |
UD-1 | Dutch submarine HNLMS O 8 |
UD-2 | Dutch submarine HNLMS O 12 |
UD-3 | Dutch submarine HNLMS O 25 |
UD-4 | Dutch submarine HNLMS O 26 |
UD-5 | Dutch submarine HNLMS O 27 |
UF-1 | French submarine Africaine (Q196) |
UF-2 | French submarine Favorite (Q195) |
UF-3 | French submarine Astrée (Q200) |
UIT-22 | Italian submarine Alpino Bagnolini |
UIT-23 | Italian submarine Reginaldo Giuliani |
UIT-24 | Italian submarine Comandante Cappellini |
UIT-25 | Italian submarine Luigi Torelli |
Post World War II U-Boats
Class | No. build | Commissioned | Notes |
XXI class | 1 | 24-02-1945 | Scuttled in 1945, Raised in 957, commisioned 1-9-1960, museum ship on 27 April 1984 |
XXIII class | 2 | 1945 | Sunk in 1945, raised again in 1956, broken up in the 60s |
201 class | 3 | 1962 | Planned 12, completed 3, Type 201 was Germany's first U-boat class built after World War II. |
202 class | 2 | 1965 | Planned 40, completed 2, Type 202 was a short lived class of very smalle submarines. |
203 class | 0 | -- | Type 203 was electric midget hunter-submarine similar to 202, Cancelled due to high cost. |
204 class | 0 | -- | Type 204 was an unrealized submarine class (similar to the Type 206) with Walter propulsion. |
205 class | 13 | 1962 | Type 205 were diesel-electric submarines, single-hull optimized Type-201 vessels. |
206 class | 18 | 1973 | 16 retired, 2 still active in de Colombian navy |
208 class | 0 | 11 | Type 208 was an unrealized hunter-submarine designed for North Sea operations. |
211 class | 0 | 11 | Type 211 (also known as TR1600) was planned but cancelled as it was financially impossible. |
212A class | 10 | 2005 | 10 still active, The Type 212A is a class of diesel-electric attack submarine |
212CD class | building 2 | -- | Type 212CD class is derived from the Type 212, but significantly larger than the 212 class. |