
The history of German frigates covers both the Imperial/Weimar/WWII era and post-war German Navy (Bundesmarine / Deutsche Marine) developments:
1. Early History (Pre-WWII):
The term “frigate” in German naval history was not widely used before WWII. The Imperial German Navy (Kaiserliche Marine, 1871–1918) mainly focused on battleships, cruisers, and torpedo boats, with smaller escort vessels often called Avisos or Küstenpanzerschiffe.
- Pre-WWI era: Germany had small scout cruisers (similar in role to frigates) for reconnaissance and protecting trade routes.
- Interwar (Weimar Navy / Reichsmarine, 1919–1935): Treaty of Versailles restrictions limited large ships, so Germany focused on smaller vessels like torpedo boats and light cruisers rather than true frigates.
2. WWII Era – Kriegsmarine:
During WWII, Germany didn’t use the term “frigate” officially; they classified ships as Zerstörer (destroyers), Korvetten (corvettes), and F-Schiffe (escort ships).
- F-class escort ships (F-Schiffe), developed late in WWII for convoy escort and anti-submarine warfare.
- Allied Lend-Lease and captured vessels were sometimes referred to as frigates by the Allies, but Germany itself didn’t adopt the term.
3. Post WWII – Bundesmarine / Deutche Marine (1949 onwards):
After WWII, West Germany (FRG) was allowed to build a new navy in 1956. This marked the modern era of German frigates.
- Key Classes:
- Type 120 (Köln-class), Commissioned: Late 1950s, Role: Anti-submarine warfare (ASW), first post-war German frigates
- Type 122 (Bremen-class), Commissioned: 1982–1990, Role: Multi-purpose frigates (ASW, anti-air, anti-surface)
- Type 123 (Brandenburg-class), Commissioned: 1994 onwards, Role: ASW-focused, long-range patrol
- Type 124 (Sachsen-class), Commissioned: 2004 onwardsRole: Air defense frigates
- Type 125 (Baden-Württemberg-class), Commissioned: 2019 onwardsRole: Stabilization, long-range deployments, low-intensity operations
- Type 126 (Niedersachsen-class), Planned to be commissioned in 2028
4. Trends and Features:
- Post-war German frigates have evolved from small ASW escorts to multi-role, high-tech vessels.
- German frigates emphasize:
- Anti-submarine warfare (ASW)
- Modern sensors and radars
- Helicopter integration
- Network-centric warfare
- Sustainability for long deployments
F class – Flottenbegleiter (Escort vessel)
The F-class escort ships were a multi-purpose class of 10 fleet escorts (Flottenbegleiter) built for the German Navy (Kriegsmarine) in the 1930s. They entered service in the late 1930s, and were rebuilt before 1940 to remedy hull structure issues caused by their over-powerful engines. In addition to escort duties, they also served as tenders and submarine training ships. They were the only ships built for the German Navy during WW2 in this role. During the Second World War, their unsatisfactory reliability and poor seakeeping abilities had them soon relegated to second-line duties in the Baltic Sea. Four ships were sunk during the war and the survivors were scrapped afterwards.

G class – Geleitenboot (Escort vessel)
The G-class escort ship project of 1941 were planned but never completed, so there are no known official service photos of that specific class in active use — only project sketches and models exist.
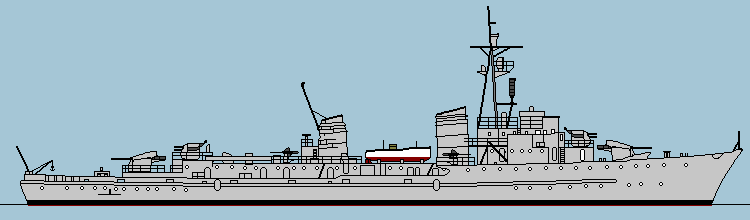
U-boot Jäger (Submarine hunter)
In the late 1930’s Germany realized a problem. Its ports, coastal routes, and invasion shipping were extremely vulnerable to enemy submarines.The big warships and destroyers were too valuable and too few to sit on boring, but vital escort and patrol duty. So the Kriegsmarine created a cheap, fast solution:The U-Boot-Jäger (submarine hunter). These ships were designed to:
Escort convoys, Guard harbors and invasion beaches, Hunt British submarines and Patrol coastal waters. In the period 1938 to 1945 many ships were build of different classes.
UJ is the prefix for a U-Boot-Jäger (Submarine Hunter). Every vessel in this category carried the UJ prefix before its number.
Class / Type | Basis / Origin | Number built / Converted | Notes |
UJ 2201 (KFK-based) | Purpose-built small ASW vessel, based on KFK fishing cutter | ~120–150 | Backbone of coastal ASW; 23–24 m long, 80–120 t; mass-produced for North Sea, Baltic, Norway, Biscay |
UJ 222 Class | Larger purpose-built steel ASW vessel | ~10–15 | 350 t, ~42 m; equipped with sonar, depth charges, and 88 mm gun; limited numbers due to shipyard constraints |
UJ 231 Class (late-war) | Late-war fast, modern coastal submarine hunter | Very few (4–6) | Designed for shallow water / coastal anti-submarine warfare; most unfinished by 1945 |
Type M40 / Minensuchboot converted to UJ | Medium minesweepers adapted for ASW | ~30–50 | 600+ t ships converted to heavy UJ roles in 1944–45 |
Converted trawlers / whalers / merchant ships | Civilian vessels converted for ASW | ~200–250 | Made up the majority of small coastal UJ numbers in early war; carried guns, depth charges, some sonar |
Captured foreign ships (Dutch, French, Norwegian, etc.) | Converted for UJ roles | ~30–40 | Used mainly in occupied waters; numbered UJ 400–500 series |
Type F120 – Köln class
The F120 Köln-class frigates were the first major warships built for the West German Navy (Bundesmarine) after World War II,
entering service in the 1960s. They were notable as the world’s first warships to feature a Combined Diesel and Gas (CODAG) propulsion system. The ships were mainly constructed for anti-submarine warfare. Six ships were built, serving from 1961 to 1989 and they all received numerous refits during their long careers. They were eventually replaced by Type 122 frigates in the 1980s with Braunschweig being the last to be decommissioned in 1989. Four ships of the class were sold to the Turkish Navy.
Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Notes |
FGS Köln | F-220 | 15-04-1961 | 17-12-1982 | Training hulk in Neustadt |
FGS Emden | F-221 | 24-10-1961 | 23-09-1983 | Sold to Turkisch Navy TCG Gemlik D-361, destroyed in a fire |
FGS Ausburg | F-222 | 07-04-1962 | 30-03-1988 | Broken up in Hamburg |
FGS Karlsruhe | F-223 | 15-12-1962 | 28-3-1983 | Sold to Turkisch Navy Gazi Osman Paso D-360. |
FGS Lübeck | F-224 | 06-06-1963 | 01-12-1988 | Sold to Turkisch navy for cannibalization |
FGS Braunschweig | F-225 | 16-06-1964 | 04-07-1989 | Sold for spare parts to Turkisch Navy in 1989 |
Type F122 – Bremen class
The F122 Bremen-class frigates were a series of eight anti-submarine warfare vessels commissioned by the German Navy between 1982 and 1990, serving as the backbone of the fleet for decades. The design was based on the proven and robust Dutch Kortenaer class but used a different propulsion system and hangar lay-out carrying two Sea Lynx helicopters. The ships were built for anti-submarine warfare as a primary task although they were not fitted with towed array sonars. They were also equipped for anti-surface warfare, while having anti-aircraft warfare point defences. This class of ship was one of the last to be constructed under post-war displacement limitations imposed by the WEU on West Germany. All eight Bremen-class frigates were replaced by the F125-class frigate.
Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Notes |
FGS Bremen | F-207 | 07-05-1982 | 20-03-2014 | Scraped in 2021 |
FGS Niedersachsen | F-208 | 15-10-1982 | 26-06-2015 | Scraped in 2021/2022 |
FGS Rheinland-Pfalz | F-209 | 09-05-1983 | 22-03-2013 | Broken up in HamburgScraped in 2017 |
FGS Emden | F-210 | 07-10-1983 | 29-11-2013 | Laid up in Wilhemshaven |
FGS Koln | F-211 | 19-10-1984 | 31-07-2012 | Sold to Scraped in 2016/2017 |
FGS Karsruhe | F-212 | 19-05-1985 | 16-06-2017 | Laid up in Kiel for blast tests |
FGS Ausburg | F-213 | 03-10-1989 | 30-06-2019 | Laid up in Wilhemshaven |
FGS Lubeck | F-214 | 19-03-1990 | 15-12-2022 | Laid up in Wilhemshaven |
Type F123 – Brandenburg class
The F123 Brandenburg class is a class of German frigate. They were ordered by the German Navy in June 1989 and completed and commissioned between 1994 and 1996, replacing the Hamburg-class destroyers. The ships primarily carry out anti-submarine warfare (ASW), but they also contribute to local anti-aircraft defenses, the tactical command of squadrons, and surface-to-surface warfare operations. Together with the F124 Sachsen-class frigates, they are the mainstay of the German surface fleet.
Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Notes |
FGS Brandenburg | F-215 | 14-10-1989 | -- | Active |
FGS Schleswig Holstein | F-216 | 24-11-1995 | -- | Active |
FGS Bayern | F-217 | 15-06-1996 | -- | Active |
FGS Mecklenburg Vorpommern | F-218 | 06-12-1996 | -- | Active |
Type F124 – Sachsen class
The F124 Sachsen class is a German Navy’s class of air-defense frigates. The design of the hull is based on that of the F123 Brandenburg class but with enhanced stealth features designed to deceive an opponent’s radar and acoustic sensors. Although designated as frigates, they are comparable to destroyers in capability. The Sachsen class frigates replaced the Lütjens class destroyers. They are similar to the Dutch De Zeven Provinciën class, in that both are based on the use of a common primary anti-air warfare system. The German government contracted for three ships in June 1996 with an option on a fourth that was provisionally to have been named Thüringen, but the option for this fourth ship was not taken up. This class was one of the most expensive ship building programs of the German Navy.
Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Notes |
FGS Sachsen | F-219 | 31-12-2003 | -- | Active |
FGS Hamburg | F-220 | 12-12-2004 | -- | Active |
FGS Hessen | F-221 | 21-04-2006 | -- | Active |
FGS Thüringen | F-222 | -- | -- | Cancelled |
Type F125 – Baden-Württemberg class
The F125 Baden-Württemberg-class frigates are a series of frigates of the German Navy. The Baden-Württemberg class is the heaviest displacement of any class of frigates worldwide. They replaced the F122 Bremen class. They are primarily designed for stabilization, crisis management, conflict prevention, and international intervention operations, asymmetric threat control at sea and support of special forces. Lack of firepower makes the ship unsuitable for major naval battle.In contrast to the Bremen class, which were built with Cold War-era scenarios in mind, the Baden-Württemberg-class frigates will have much enhanced land-attack capabilities. This will better suit the frigates in possible future peacekeeping and peacemaking missions.
Name | Class | Commissioned | Decommissioned | Notes |
FGS Baden-Württemberg | F-222 | 17-06-2019 | -- | Active |
FGS Nordrhein-Westfalen | F-223 | 10-06-2000 | -- | Active |
FGS Sachsen-Anhalt | F-224 | 17-05-2021 | -- | Active |
FGS Rheinland-Pflatz | F-225 | 13-07-2022 | -- | Active |
Type F126 – Niedersachsen class
F126 or Niedersachsen-class frigate is a planned German frigate class intended to replace the F123 Brandenburg-class frigates in the German Navy. The ships are to be the largest surface warships to join the German Navy since World War II. The first ship, Niedersachsen, is planned to be commissioned in 2028, with Saarland, Bremen, and Thüringen to follow. On 8 April 2024, Germany exercised their option and purchased an additional two frigates. The contract for two additional F126 frigates was signed on 19 June 2024.The class is to be mission modular and is capable of accommodating so-called mission modules which include devices, space, sensors and weaponry necessary to carry out a given task optimally. If not in use, the modules can be maintained and replaced separate from the ship and also be exchanged between different ships in the class. The ships are planned to replace the Brandenburg class in their anti-submarine warfare (ASW) role. Similar to the Baden-Württemberg class however, they will also be able to stay at sea for up to two years without requiring maintenance at port, with crews rotating to and from the deployed ship every four months. This capability is expected to allow for a more efficient use of hulls by reducing the time spent during transfer from Germany to conflict zones such as the sea off the Horn of Africa where German ships repeatedly took part in counter-piracy missions.


































